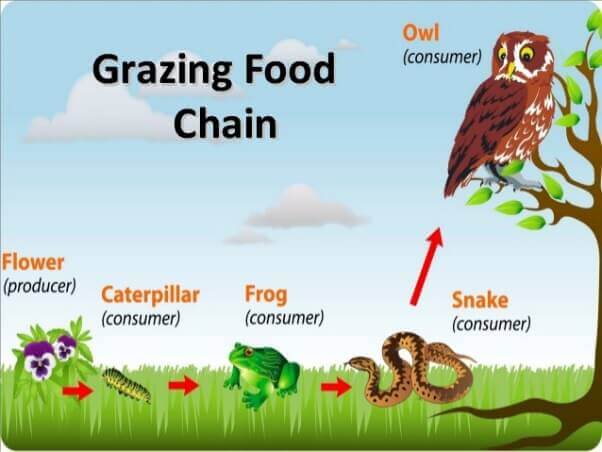
Why Do Food Chains Rarely Have More Than Five Stages Biology Diagrams Food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. Learn more about food chains in this article. Detritus food chain: The detritus food chain includes different species of organisms and plants like algae, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, mites, insects, worms and so on. The detritus food chain begins with dead organic material. The food energy passes into decomposers and detritivores, which are further eaten by smaller organisms like carnivores.

What Is A Food Chain? The food chain is a series of creatures that begins with producer organisms, having consumers at various levels in between, and ends with decomposer species. A food web connects numerous food chains. The food chain takes a single path, whereas the food web takes several paths. The food chain teaches us about the relationships between creatures. Food chains and food webs are related but not identical concepts. While a food chain is a linear sequence of energy transfer, a food web is a more complex, interconnected network of food chains. Food webs better represent the complexity of ecosystems, where most organisms consume multiple types of food and are preyed upon by various predators.

Definition, Types, Parts, Examples Biology Diagrams
A food chain refers to the sequence of events in an ecosystem in which one living organism consumes another, which is then consumed by a larger organism. Food Chain - Definition, Types, Parts, Examples. By Sourav Pan Published on March 24, Decomposers finish a cycle of life. They help recycle nutrients because they add nutrients to Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples, and Diagram. (through the phosphorus cycle), and carbon (through the carbon cycle) back into the atmosphere. The detritus food chain is very important for nutrient recycling in the ecosystem.
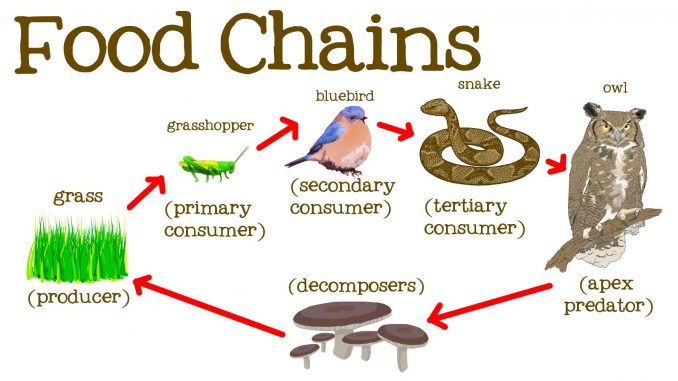
Definition of Food Chain. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each organism serves as a source of food for the organism at the next trophic level, demonstrating the transfer of energy and nutrient in an ecosystem. What is Food Chain? A food chain represents the flow of energy and nutrients among different organisms in an In an ecosystem, plants and animals all rely on each other to live. Scientists sometimes describe this dependence using a food chain or a food web. Food Chain A food chain describes how different organisms eat each other, starting out with a plant and ending with an animal. For example, you could write the food chain for a lion like this: